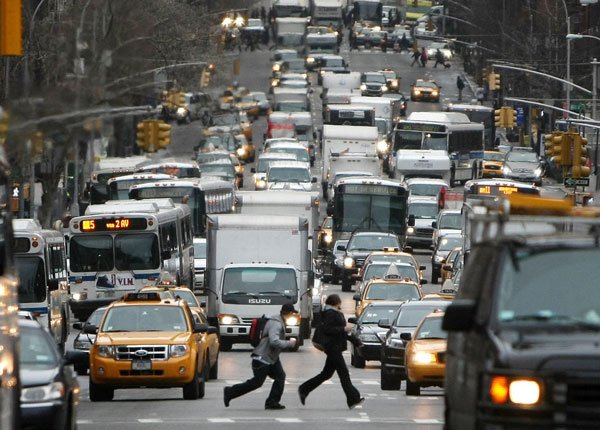
Rules of The Road 2022: Right-of-Way, Passing, Speed & Driving Laws
Updated May 30, 2022The term “rules of the road” covers every traffic law, regulation and recommended driving practice established by a state government or federal transportation authority, with the aim of keeping road users safe and the Highway Transportation System running in an orderly manner.
The evolution of the automobile has led to the rapid development of traffic laws and road rules over the past century, many of which are continually being adapted and fine-tuned to suit our nation’s ever-growing transportation system. Private vehicles like cars, light trucks, vans and motorcycles now account for 91 percent of all personal travel. Without rules of the road, the entire country would descend into chaos in a matter of hours.
You have a lot to learn as a new driver but do not worry; if millions of other motorists can get to grips with the rules of the road, so can you! This essential block of articles begins with an introduction to rules of the road, including:
First up, let’s start by summarizing all the core topics we will be covering in this section. Happy studying!
Rules to coordinate traffic flow
Understanding “traffic flow” is an important piece of the puzzle when learning about road rules, how they work and why they have been established. All rules of the road are put in place to protect road users or keep traffic flowing smoothly. In fact, most traffic laws and road rules check both these boxes, as what maximizes traffic flow usually minimizes the risk involved with driving on a stretch of roadway – and vice versa!
When all traffic occupying a roadway is evenly spaced and traveling at a similar, consistent speed, there is less opportunity for conflict between vehicles, or between vehicles and pedestrians. Plus, smooth-flowing traffic allows everybody to reach their destinations in a timely, stress-free manner. The Federal Highway Administration and state transport authorities have implemented carefully considered traffic rules to optimize traffic flow and keep every road user safe. As a new driver, it is your responsibility to learn and abide by these rules.
Our “rules of the road” section kicks off by discussing traffic flow and the techniques used to coordinate it. In addition to learning how to control your own vehicle and obey traffic laws, you must learn to communicate and cooperate with other road users effectively.
Right-of-way rules
“Right-of-way” informs practically every interaction between road users you will experience or witness when driving on public roadways. Whenever more than one vehicle or pedestrian wishes to pass over the same area of pavement at roughly the same time, right-of-way laws come into play and determine who gets to go first and who must “yield” the right-of-way.
Right-of-way can seem like a confusing concept when you first begin learning to drive but in truth, getting to grips with the basics is easy. We explore everything you must know about right-of-way rules in different driving situations across ten, detailed articles. With this material and your trusty driver’s handbook, you will learn how right-of-way applies at intersections, pedestrian crossings, roundabouts and railroad crossings. We also cover essential right-of-way laws for “special” road users, such as school buses and emergency response vehicles.
In practice, motorists do not have a great deal of time to consider the finer details of right-of-way law when faced with an unfamiliar or unexpected situation. Generally speaking, you will never go far wrong if you keep these basic rules in mind:
- 1

b'You do not lawfully have right-of-way unless another person yields it to you.'
- 2

b'Always 'b'scan the roadway'b' before proceeding, even if the right-of-way should be yours. Other drivers may break the rules.'
- 3

b'Traffic already on an intersection, roundabout, highway or another public road should always have right-of-way over vehicles seeking to enter from another road, driveway, side street or parking spot.'
- 4

b'If in doubt about what to do in a right-of-way conflict, YIELD. Giving up the right-of-way is nearly always the safest choice.'
Rules for passing and being passed
The practice of passing other vehicles is risky at the best of times and can be incredibly dangerous if executed incorrectly. Vital passing rules and associated traffic laws are covered in this section. Motorists should only seek to pass another vehicle if doing so is the SAFEST option; for instance, if the driver in front of you is having vehicle trouble or is driving much slower than other traffic. Before passing any vehicle, drivers must:
- Check road signs, pavement markings and call upon their road-rule knowledge to make sure passing is allowed
- Make sure they have enough space to execute the pass
- Communicate their intention to pass using indicator lights or hand signals
Your behavior while being passed by another motorist is almost as important as what you do while passing a vehicle yourself. Any driver being passed must do everything in their power to help the other motorist execute the maneuver safely. This topic is covered in more detail in part two of the “passing rules” section.
Stopping and parking rules
Some parking rules are applicable everywhere, while others vary based on individual state and city laws. To practice safe and lawful parking, new drivers must first learn the legal distinction between “stopping”, “standing” and “parking”, as they are three different actions. In some places, one or more of these actions are prohibited while others are allowed.
Our course will talk you through the essential differences between stopping, standing and parking so that you can successfully negotiate and abide by the law. The two articles in this sub-section also deal with choosing a safe parking spot by the road or in a parking lot, leaving your vehicle and how to exit a parking spot safely.
Speed laws and regulations
Speed laws and regulations affect drivers on every journey, usually on multiple occasions. The speed at which we drive has an enormous influence on traffic flow and public safety. For this reason, every roadway in the United States is controlled by speed laws. This always includes a maximum speed limit, which will either be stated on regulatory road signs or “assumed” based on the type of road it is. Some high-speed roads are also controlled by a minimum speed limit.
Speed limits depend on the risk associated with the roadway. In general, complex or high-risk environments have lower maximum speed limits. You must know how to identify the speed limit on any stretch of roadway, as there will not always be regulatory speed limit signs to guide you. We provide an overview of speed limits in different areas and situations around the United States, though you must also refer to your state’s driver manual, as the rules often vary from state to state.
Choosing a safe and appropriate speed at which to drive is not simply a matter of sticking within the legal speed limit. Drivers must always keep in mind that speed limits are set with ideal driving conditions in mind. If motorists on a roadway are exposed to greater-than-usual risk, they must lower their speed to a safe level or risk prosecution for dangerous driving. “Driving at reduced speeds” covers everything you must know about this issue to stay safe and operate your vehicle within the boundaries of the law.
Seat belt laws and regulations
Wearing your seat belt is not optional – it is required by law. Adults will be fined if caught not wearing a seat belt, while drivers will be held responsible for any underage passenger in their vehicle who is caught not wearing a seat belt or an age-appropriate restraint. This is true in every state, though seat belt law details and punishments for violating the law differ across the country.
The risk of being injured or killed in a car crash sky-rockets for any driver or passenger not wearing a seat belt. As a result, seat belt laws are widely advertised and enforced with the nationwide “Click it or Ticket” campaign. Sadly, receiving a ticket is one of the best-case scenarios if you fail to buckle up. Seat belts save lives and must always be worn – end of story.
There is a great deal of confusion surrounding child restraint laws, as they differ slightly from one state to the next. Federal law simply states that all children must be restrained in an approved car seat which is appropriate for their age, size and weight, when traveling in a motor vehicle. Rear-facing seats, forward-facing seats and booster seats are all designed for different developmental stages. Drivers must refer to state law and the car seat manufacturers guidelines when choosing and installing a child restraint. The information in this article will help you navigate car seat rules and make the right decision.
Cell phone laws
Regardless of the law, operating a cell phone or similar communication device while driving is a bad idea. An alarming number of accidents and collisions happen because a driver was talking on the phone, texting or otherwise distracted by their cell. As teen drivers are more “at-risk” than older drivers, many states impose stricter cell phone laws on minors than they do on adults. As with most traffic laws, the rules concerning cell phones and other wireless communication devices differ quite dramatically from one state to the next.
Due to the level of risk involved in each activity:
- Talking on phone with a hands-free system is more widely permitted than using a hand-held device.
- Talking on the phone in general is more widely permitted than texting while driving – which is illegal in most states.
Check out your official driving handbook to figure out cell phone laws in your area. Motorists who use a cell phone inappropriately while driving will be stopped and cited.
Dealing with traffic law enforcement
Most new drivers do not put much thought into how they should behave if a law enforcement officer pulls them over, despite it being such an important issue. Somewhere along the line, you are bound to be pulled over by a police officer – it happens to everybody. How you react to being pulled over will determine whether the interaction runs smoothly for everyone involved, or whether it becomes a stressful and upsetting experience. The most important rules to remember are:
- 1

b'Signal your intention to comply with the officer by activating your turn indicator or using the appropriate hand signal.'
- 2

b'Roll your window down, place your hands on the steering wheel (without holding anything else in your hands) and wait for the officer to approach.'
- 3

b'Do not reach or search for your license, registration or insurance documents without first telling the officer where they are.'
- 4

b'If you are given a citation for a traffic violation, sign for it and do not argue. You will have the opportunity to dispute the citation later if you feel it was unjustly issued.'
“Traffic Law Enforcement” includes a detailed explanation of your rights during a traffic stop and how to stay safe if you believe you are in danger. Make sure you read this information thoroughly. We also discuss the multitude of different reasons why a law enforcement officer may stop you, as it does not always mean you have committed a traffic violation.
Rules for dangerous driving situations
The penultimate article in “Rules of the Road” covers some basic driving rules to help you stay safe in high-risk environments. Despite what you may think, high-risk driving situations are a common occurrence! Most drivers must deal with poor visibility, high-speed roadways or less-than-favorable traction on a regular basis. How often are you likely to drive on highways, mountain roads, at night or in bad weather? Even if you manage to avoid all these high-risk situations, you will sometimes be endangered by the actions of other drivers – there is no way to avoid it.
Learning to identify hazards and risks in any driving environment is essential if you hope to become a safe and responsible driver. Then, you must know how to alter your behavior to mitigate these risks. A brief introduction to risk in different situations is provided here. Later, in “Complex Driving Environments” and “Hazardous Conditions”, high-risk driving situations are explored in greater detail.
Other important traffic laws
To round off this block, we explore miscellaneous traffic laws and regulations that every motorist must know. If you are a teen driver, keep in mind that your actions in everyday life can affect your driving privileges. Many states have laws that allow for the suspension or delay in issuance of a minor’s driving permit, if that minor exhibits poor performance or behavior in school, uses a firearm unlawfully or is convicted of vandalism.
This section also covers driving behaviors that are universally illegal, such as littering, abandoning animals, vehicle theft and driving away from a gas station without paying for gasoline. Additionally, we explore traffic laws and regulations for actions that are illegal in some states or under certain conditions, such as leaving children in parked vehicles, riding in trailers and transporting cargo. You can avoid inadvertently breaking the law by making sure you are up-to-speed with this information!