Seat Belt Laws & Regulations for Child Restraints: Car Seat or Booster Seat?
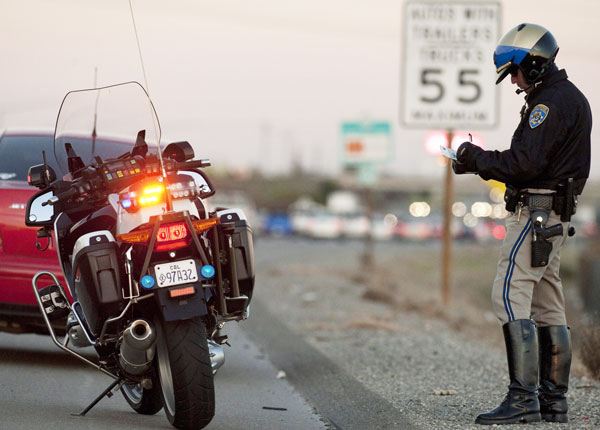
Updated Oct. 20, 2020Children and infants must be restrained in an age-appropriate, federally approved car seat when traveling in any passenger vehicle. Standard seat belts are designed to protect adults; children may be insufficiently secured or injured by an ordinary seat belt in a car accident.
The laws concerning child restraints have been fine-tuned considerably over the past few decades, leading to a much higher standard of child safety. NHTSA statistics indicate that when correctly installed, child car seats cut back the risk of fatal injury in young children by 54 percent and babies under one year old by 74 percent.
It is the responsibility of all drivers to ensure that any underage passengers they carry are properly secured. The safety of children in your care depends on any child restraint system you use being correctly installed. Always follow the manufacturer’s installation instructions when securing and using a child safety seat.
Child restraint laws
Before we discuss child restraint laws in any detail, it is important to note that driving rules differ slightly from one state to the next. The best source of information on child restraint laws in your state is the official driver’s handbook – be sure to refer to it when choosing an appropriate car seat.
The point at which a minor is responsible for his or her own restraints varies too. In Texas, drivers are responsible for ensuring all passengers under the age of 17 are wearing a seat belt or an appropriate child restraint. Though in Florida, Pennsylvania and many other states, drivers are responsible for all passengers under 18. You can find this information in your driving manual.
Car seat or booster seat?
Whether an underage passenger requires a car seat, or a booster seat, is determined by their age and height. In Texas and California:
- 1

All children under the age of two must be secured in a rear-facing car seat unless they are more than 3 feet 4 inches tall.
- 2

All children under the age of eight must use a booster seat, unless they are 4 feet 9 inches or taller.
There may be slight variations in these rules around the United States – check your driver’s manual. Though, as these laws are dictated by scientific testing and federal safety standards, you are unlikely to encounter any significant differences. The main point to take away from this is that as a child grows, their safety requirements change. We can break these changing child restraint rules down into “phases”, as discussed below.
Phase 1: Rear-facing seats
Rear-facing car seats may be used for infants from birth and should continue to be used until that child surpasses the maximum height and/or weight limit set by the manufacturer. Rear-facing car seats must always be installed in the back seat of the vehicle.
Phase 2: Forward-facing seats
Children must graduate to a forward-facing car seat when they outgrow their rear-facing seat. Never secure a child into a forward-facing car seat until they meet the minimum height and weight requirements set by the manufacturer. Child restraint laws generally state that a child must be at least two years of age before using a forward-facing seat. You should continue using a forward-facing seat for your child until they grow tall enough to require a booster seat.
Phase 3: Booster seats
Children aged four years and over who meet state and manufacturer-established height requirements should be secured with a booster seat, using the standard adult lap and shoulder seat belt. As a child using a booster seat can move or release the standard seat belt themselves, behavior and maturity must also be considered.
Phase 4: Adult safety belt
When children meet the minimum height requirement to use an adult seat belt, you may secure them using the lap and shoulder belt without a booster seat. As mentioned above, the minimum height requirement in most states is 4 feet 9 inches. Most children reach this height at around 10 to 12 years old, though there are exceptions. Make sure the lap belt is positioned over the child’s hips or thighs, while the shoulder belt is positioned directly across the chest and shoulder without pressing on the child’s neck.
Children must ride in the back seat
Consider these positioning rules when installing a child restraint system:
- Children restrained in forward or rear-facing car seats must NEVER ride in the front seat.
- Booster seats can be used in the front seat of a vehicle when necessary.
The law in most states says that children must ride in the back seat if there is space available, as the back seat is always safer. This refers to children under 13 years old in Texas and children under 8 years old in New Jersey. There may be a different age limit in your area – check this out in your driving manual. Most state driver’s handbooks stipulate that children may ride in the front seat if all back seat positions are occupied by younger children.