Car Battery Problems & Solutions: Jump Starting A Car, Battery Replacement
Updated Dec. 31, 2020Your car battery is designed to supply a short burst of power to the engine to get it going. The rest of your car’s electrical systems such as lights, transmission controls, audio and climate control can run off the battery, but only for a very short time. The engine itself will power these systems and re-charge the battery when it kicks in.
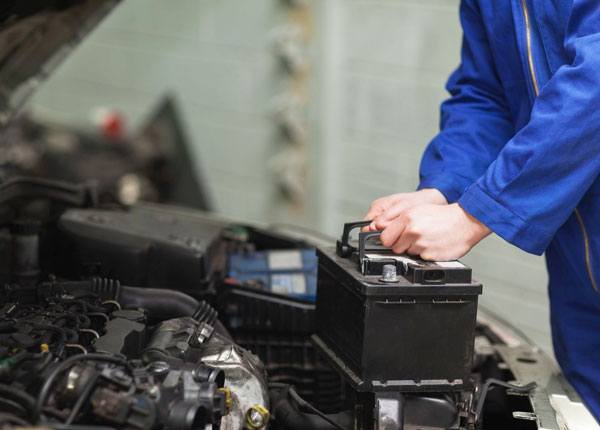
Despite the one, very brief job your car battery must fulfill, it is easily the most important component of your vehicle. Without a functional battery, the engine cannot start. Drivers must learn how to look after their vehicle’s battery and avoid wearing it out. Running your engine for very short periods is extremely bad for the battery, as you will deplete its power without allowing it time to recharge.
Common battery problems
If your car engine cranks but doesn’t start, or does not crank at all, you are probably dealing with a dead battery. Understanding what can lead to a dead battery will help you avoid this frustrating situation. The following issues can contribute to a battery malfunction:
- 1

Leaving headlights on.
Your car’s battery is only capable of running electrical features such as headlights for a very short time. If you accidentally leave your lights on overnight, you will be waking up to a dead battery in the morning. - 2

Electrical problems.
Faulty wiring and other electrical issues can lead to “parasitic drain” whereby power is leached from the battery even when the ignition is turned off. Regular battery problems could be a symptom of electrical problems. - 3

Faulty charging system.
If your car battery continues to lose charge even while you are driving, a faulty charging system is likely to blame. - 4

Very hot or cold weather.
These conditions can extend the time it takes your battery to fully charge, or prevent it from charging altogether. Check for corrosion and other problems more frequently during periods of extreme temperature. - 5

Many short journeys.
This places strain on the battery and does not allow it sufficient time to recharge. - 6

Corrosion.
Your battery cables may be loose or corroded if the car does not start easily, or the battery does not recharge efficiently. Dirt and corrosion can be cleaned from your battery with a toothbrush or rag.
Symptoms of battery problems
Your car battery may be on its way to failing if you notice any of the signs listed below. A mechanic will be able to load-test your battery and diagnose the problem if there is one.
- Your headlights appear dimmer, with no obvious mechanical cause.
- Your engine cranks slower than usual.
- Your car backfires. A failing battery can throw off sparks that lead fuel to build-up in the car’s cylinders. When this fuel is ignited the car will backfire. This is a warning sign you do not want to ignore!
- A “clicking” sound when you turn the key in the ignition. This could indicate a weak electrical current being sent to the starter.
How to jump-start a vehicle
If your car will not start because your battery is dead, you may be able to jump-start it with jumper cables and another running vehicle. Jump-starting transfers charge from another vehicle’s functional battery to get your engine running, which will then recharge the battery. This is only advisable if the battery has been run down (e.g. if headlights were left on overnight) and is not obviously in need of repair.
Keep in mind that not all vehicles can be jump-started. You must check your vehicle owner’s manual before attempting to jump-start your car. Jump-starting is not suitable for all vehicles as it may cause damage to certain electrical systems, especially if it is not done correctly.
If you are certain it is safe, you may attempt to jump-start your car with these instructions:
- 1

Get your hands on some jumper cables – keeping some in the trunk is a good idea.
You will also need somebody with a running car. - 2

Park the running car nose to nose with your car, so that the engines are close.
Otherwise, the jumper cables may not be long enough to reach between both batteries. - 3

Make sure both cars are turned off before fixing the jumper cables.
Engage both parking brakes and activate your hazard lights. - 4

Next, attach the red jumper cable clamps.
They should fix to the red, “POS” or “+” terminal on the dead battering, then to the functional battery in the other vehicle. - 5

Attach the black cable clamps.
Fix these clamps to the black terminal on the functional battery, it may also be labeled “NEG”. The other end of the black cable must be clamped to an unpainted, metal part of your car’s engine. - 6

Start the assisting car and let it run for a few moments to charge the dead battery.
- 7

Attempt to start your engine
If this does not work, rev the other engine and repeat this step. - 8

Disconnect the black clamps first, then the red clamps.
Keep your car running and take it for a drive to continue recharging the battery.
Seeking roadside assistance
If jump starting is not suitable for your car or you were not able to get your engine started, your only option is to seek roadside assistance. Emergency responders may be able to get your car started by the roadside and if not, they will drive you to a mechanic.
Depending on where you break down, there may be free roadside assistance available! For instance, the California Highway Patrol (CHP) offers a free roadside assistance service that can be reached during an emergency by calling 911 or a direct dispatch line in less urgent cases. Details of any such services will be in your state’s own driving manual.
Replacing a car battery
Your car battery should be replaced once every few years. Most batteries will become completely unreliable once they are five or six years old. It is important to replace your car battery promptly, as soon as you are aware that it is beginning to fail. Otherwise, your malfunctioning battery could damage other vital parts and systems and end up costing you more money.